
|
 |
 |
Saturation Work
The maximum value of acoustic pressure within an ultrasonic beam is limited by acoustic
saturation. The theoretical basis for acoustic saturation has been analyzed previously.
In this work, a high-power pulse source is used to drive acoustic pressure levels from an
ultrasonic beam to saturation. An automatic procedure determines the field's beam axis
using a calibrated Marconi PVDF hydrophone. The hydrophone measured RF waveforms are
recorded along the beam axis and analyzed off-line. The peak compressional pressure is
evaluated as a function of distance along the beam axis. The overall maximum pressure is
compared to theoretical predictions. Three-, six-, and nine-MHz center frequency,
19-mm-diameter transducers were analyzed. The longer focal length transducer saturation
level was comparable to a theoretical prediction. However, the theoretical saturation
level for the shorter focal length transducers underestimated experimental results.
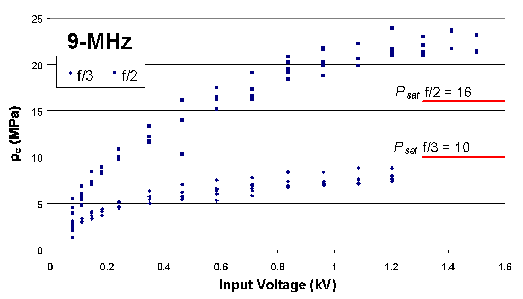
Below is a plot of peak compressional pressure vs. applied voltage for a 9-MHz f/2 and
9-MHz f/3 transducer. Also indicated is the theoretical prediction Psat.
BRL Projects >>


|
 |

